| This document is derived from an original post by Tim Dysinger. However, the examples here are for nng instead of nanomsg. For the legacy nanomsg version of this, see Getting Started with 'nanomsg'. |
Bus (Routing)
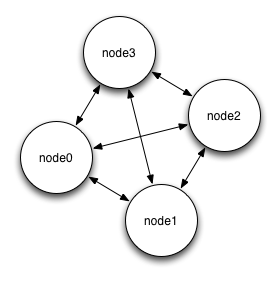
The bus protocol is useful for routing applications, or for building fully interconnected mesh networks. In this pattern, messages are sent to every directly connected peer.
bus.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <nng/nng.h>
#include <nng/protocol/bus0/bus.h>
void
fatal(const char *func, int rv)
{
fprintf(stderr, "%s: %s\n", func, nng_strerror(rv));
exit(1);
}
int
node(int argc, char **argv)
{
nng_socket sock;
int rv;
size_t sz;
if ((rv = nng_bus0_open(&sock)) != 0) {
fatal("nng_bus0_open", rv);
}
if ((rv = nng_listen(sock, argv[2], NULL, 0)) != 0) {
fatal("nng_listen", rv);
}
sleep(1); // wait for peers to bind
if (argc >= 3) {
for (int x = 3; x < argc; x++) {
if ((rv = nng_dial(sock, argv[x], NULL, 0)) != 0) {
fatal("nng_dial", rv);
}
}
}
sleep(1); // wait for connects to establish
// SEND
sz = strlen(argv[1]) + 1; // '\0' too
printf("%s: SENDING '%s' ONTO BUS\n", argv[1], argv[1]);
if ((rv = nng_send(sock, argv[1], sz, 0)) != 0) {
fatal("nng_send", rv);
}
// RECV
for (;;) {
char *buf = NULL;
size_t sz;
if ((rv = nng_recv(sock, &buf, &sz, NNG_FLAG_ALLOC)) !=0) {
if (rv == NNG_ETIMEDOUT) {
fatal("nng_recv", rv);
}
}
printf("%s: RECEIVED '%s' FROM BUS\n", argv[1], buf); (1)
nng_free(buf, sz);
}
nng_close(sock);
return (0);
}
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if (argc >= 3) {
return (node(argc, argv));
}
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: bus <NODE_NAME> <URL> <URL> ...\n");
return 1;
}| 1 | Blithely assumes message is ASCIIZ string. Real code should check it. |
Compilation
gcc bus.c -lnng -o busExecution
./bus node0 ipc:///tmp/node0.ipc ipc:///tmp/node1.ipc ipc:///tmp/node2.ipc & node0=$!
./bus node1 ipc:///tmp/node1.ipc ipc:///tmp/node2.ipc ipc:///tmp/node3.ipc & node1=$!
./bus node2 ipc:///tmp/node2.ipc ipc:///tmp/node3.ipc & node2=$!
./bus node3 ipc:///tmp/node3.ipc ipc:///tmp/node0.ipc & node3=$!
sleep 5
kill $node0 $node1 $node2 $node3Output
node3: SENDING 'node3' ONTO BUS node0: SENDING 'node0' ONTO BUS node1: SENDING 'node1' ONTO BUS node2: SENDING 'node2' ONTO BUS node0: RECEIVED 'node1' FROM BUS node1: RECEIVED 'node0' FROM BUS node2: RECEIVED 'node0' FROM BUS node3: RECEIVED 'node1' FROM BUS node0: RECEIVED 'node2' FROM BUS node1: RECEIVED 'node2' FROM BUS node3: RECEIVED 'node2' FROM BUS node0: RECEIVED 'node3' FROM BUS node2: RECEIVED 'node3' FROM BUS node1: RECEIVED 'node3' FROM BUS node3: RECEIVED 'node0' FROM BUS node2: RECEIVED 'node1' FROM BUS